Quantum Computing With Wiweeki
What Is a Quantum Computer?
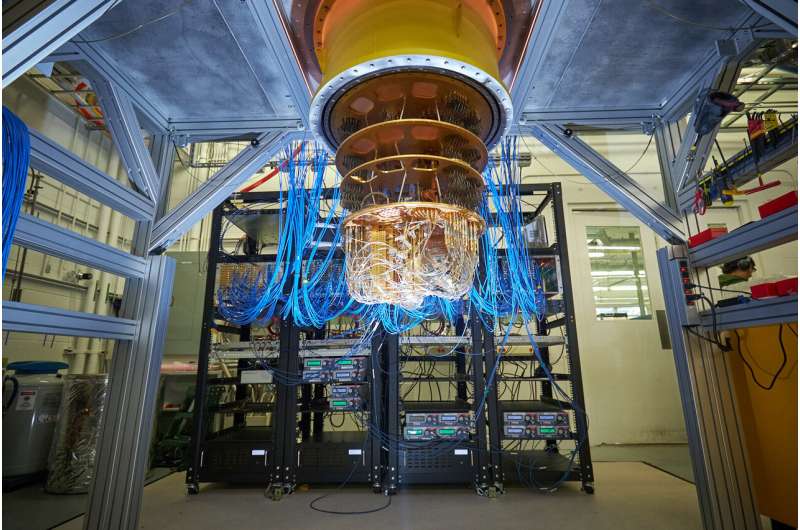
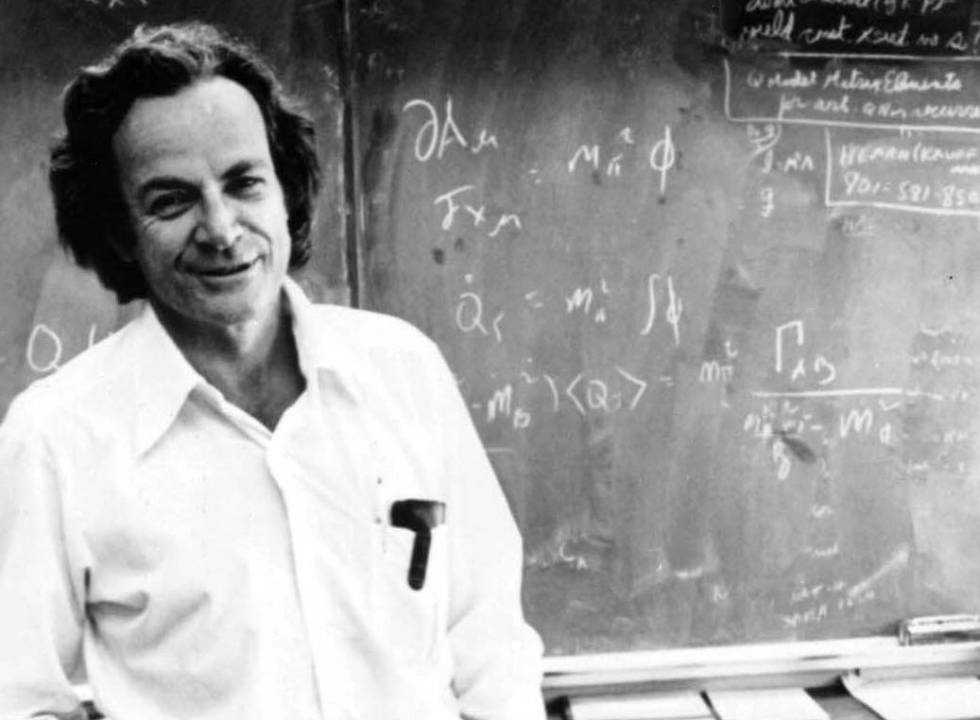
Quantum Computing is a new, revolutionary way of computing which harnesses the powers of physics and computer science to bring massive leaps in computational power. The idea of a quantum computer arose in 1982 when the physicist, Richard Feynman, proposed his solution for analyzing the way in which the elements in the electro-magnetic spectrum behave and how they interact – the quantum computer.
So, why couldn’t he use a classical computer to analyze these electrons and photons? This is because the quantum systems that physicists wish to investigate have millions of electrons, therefore an unimaginable number of probabilities that a classical computer could never keep up with. Feynman thought, however, a quantum computer would simulate quantum behavior as it would have occurred in nature. Feynman states, “Nature isn’t classical, dammit, and if you want to make a simulation of nature, you’d better make it quantum mechanical, and by golly it’s a wonderful problem, because it doesn’t look so easy.” The idea of combining nature with technology to have optimal computing power has led to today’s race to achieve “quantum supremacy”.
The Powerful Quantum Computer
How does a quantum computer have so much power? The answer lies in the three main properties of the quantum computer: Qubits, Superposition, and Entanglement.
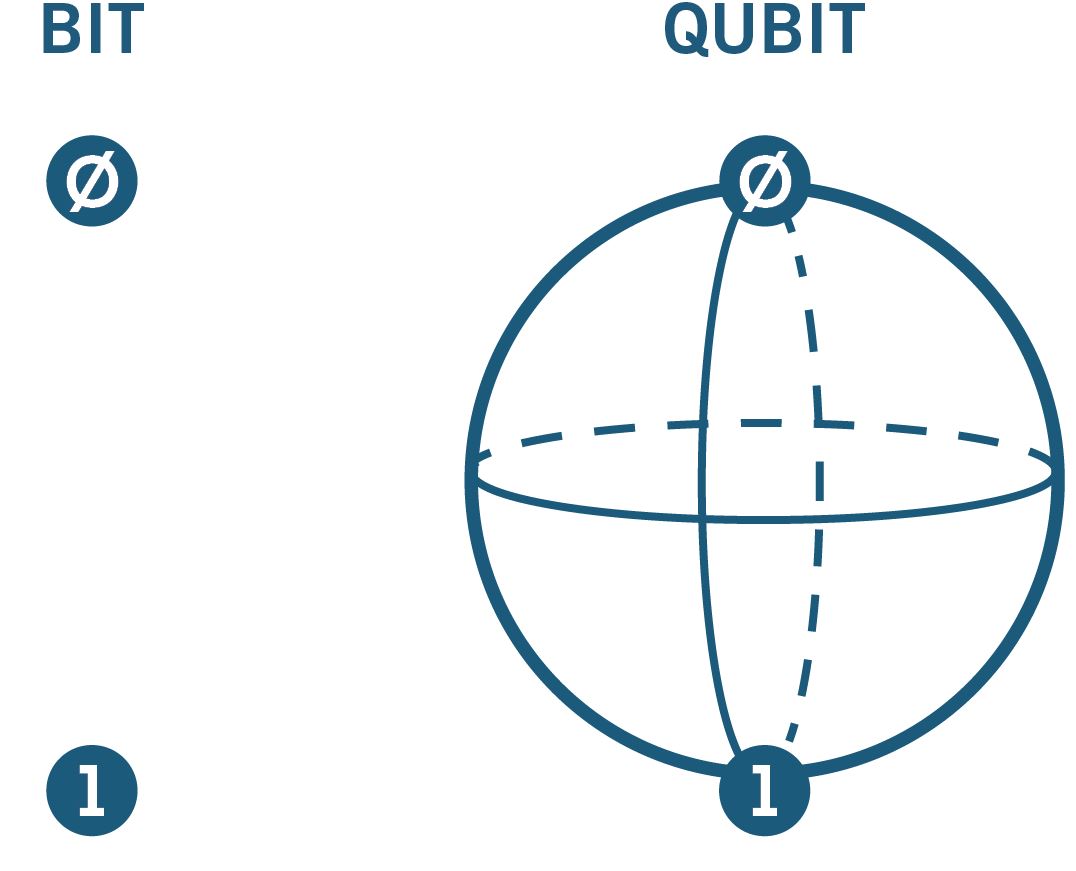
Classical computers have information encoded in bits, where each bit is either 0 or 1. Quantum computers have information encoded in quantum bits, or, qubits. A qubit is a two-level quantum system, where it can have a value of both 0 and 1 at the same time. This phenomenon is known as superposition and is one of the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics because it helps eliminate the restraints of the classical bit.
Watch this TedTalk given by Shohini Ghose for an excellent example of how qubits and superposition works.
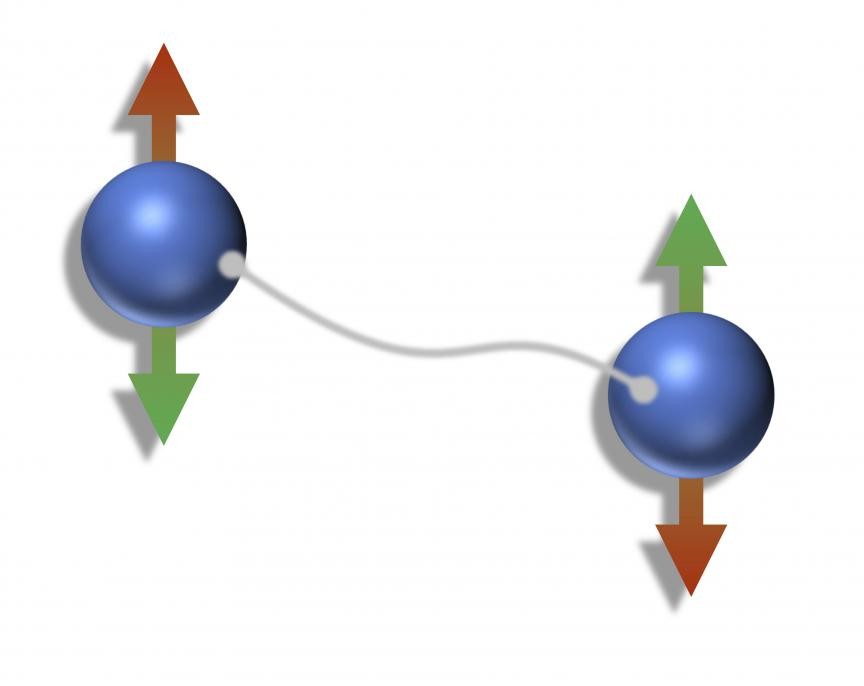
Entanglement is another fundamental principle of quantum mechanics that shows the shear power of quantum computers. Entanglement occurs when two particles are strongly correlated and they interact with each other to create a single, unified quantum state. This means that measurements of one particle will affect the other, regardless of distance between each other, and, if you have the information on one qubit, you have the information on all qubits it is entangled with. Therefore, the process of entanglement exponentially speeds up the computation processes, allowing the quantum computer to compute extremely complex systems.
You can learn more in depth about qubits, superposition, entanglement, and more in The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Quantum Computing and its Applications.

Quantum Computer vs Super Computer
Until now, supercomputers have been used to crunch high quantities of data by overloading them with thousands and thousands of classical GPUs and CPUs. Because they only work through regular bits and not quantum bits, their processing power caps at 2n bytes, while quantum computers cap at an immense nn bytes. In fact, Google\’s quantum computer is about 158 million times faster than the world’s fastest supercomputer! However, the goal of creating quantum computers is not to replace supercomputers. Quantum computers are a new technology that will be used to solve complex problems at a molecular level utilizing probabilities and uncertainty.
Solving Problems with Quantum Computing
We know the goal of the quantum computer is to be able to solve complex problems, but what kind of problems will they solve? Since quantum computers are still in their infancy, there is still some uncertainty regarding what they will be able to achieve. However, that does not stop us from thinking of the endless possibilities.
For example, machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies will improve exponentially, such as weather predictions. Weather models have thousands of points to process (air quality, air pressure, temperature, etc.) and with today’s current computation power, it takes at least 24 hours to process those models. “As you collect more and more data, these current computer models are not able to give useful information as quickly as possible, so a quantum computer has that ability. It can compute, a lot faster, all of these big problems,” says Venkatesh Kalluru, CTO of Wiweeki, LLC, “so quantum computers are going to come and save the world. That’s what the future is betting on right now.”
Learn more about the Top Applications Of Quantum Computing Everyone Should Know About.
Wiweeki and the Quantum Computer
Because quantum computers are not widely available, Wiweeki still has so much to learn. To make good use of a quantum computer, Wiweeki is working towards accessing petabytes worth of data to apply to quantum computing with the goal of getting ahead of the curve and being the first to get there. “We want to be on the bleeding edge, not the cutting edge” says Mr. Kalluru. The difference? The bleeding edge is the breakthrough, the cutting edge just keeps it going. Wiweeki will be a part of that breakthrough.
There is no doubt that quantum computers will change the way Wiweeki develops solutions for their customers. Applications will run faster, models will make faster and more accurate predictions, and large volumes of data will be processed faster. When Wiweeki gets their hands on a quantum computer, the next part of their journey will be exciting and innovative, changing the future of IT.
Learn more about Wiweeki’s current Services.
Wiweeki\’s Fascination with Quantum Computers
The ideas surrounding quantum computers offer us mystery and uncertainty. We will never know for certain what the future holds for quantum computing, but it’s that uncertainty that makes quantum computers scary and exhilarating all at the same time.
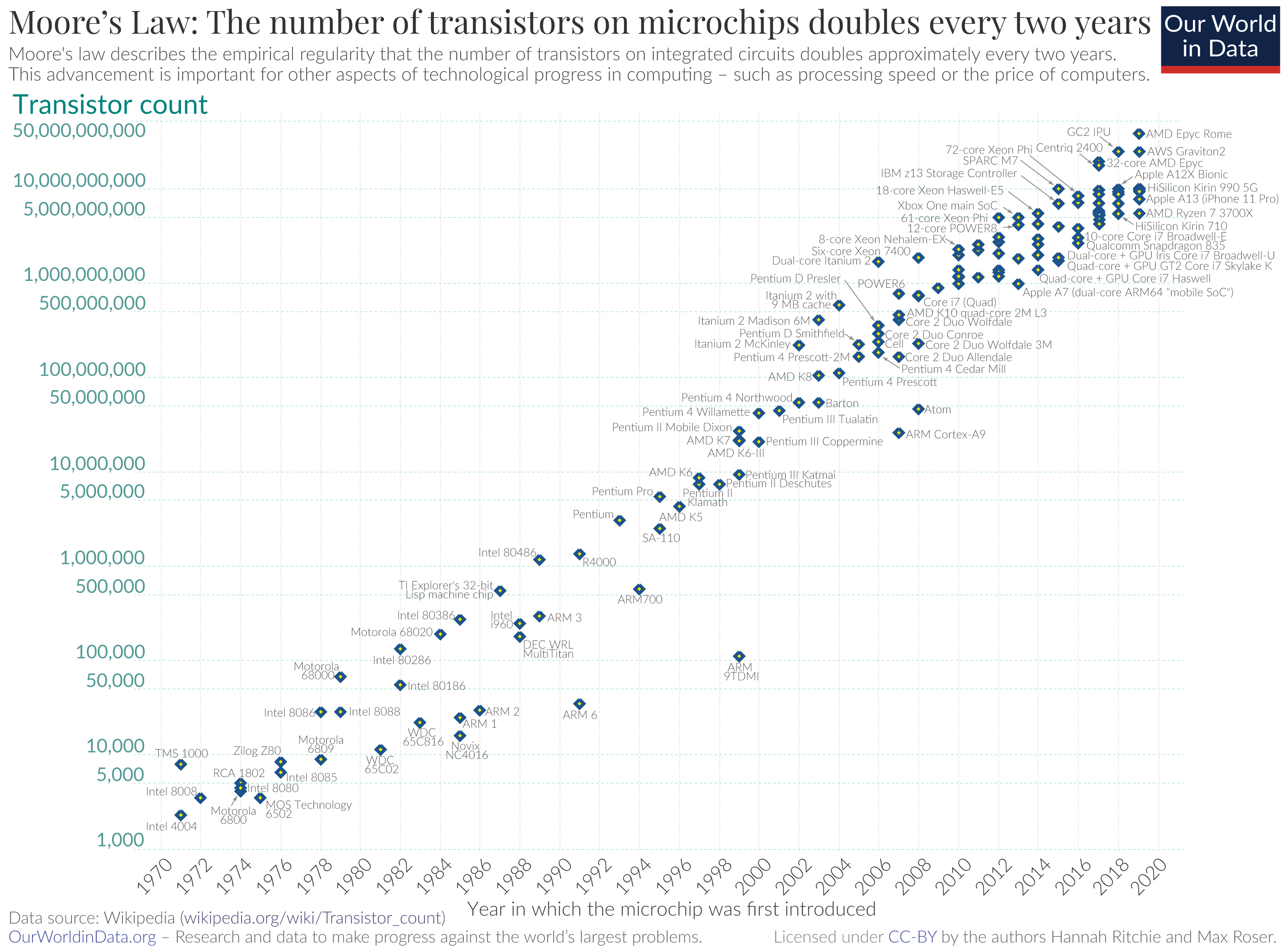
For Wiweeki, the fascination lies in the search for a faster processor. Moore’s Law says the speed of the computer will double every two years. The prediction was made in 1965, and is still accurate today. According to Mr. Kalluru, “The fascination is in that Moore’s Law is not going to stop, it’s going to continue to grow.”
In fact, quantum technology is growing so rapidly that Moore’s Law is no longer enough to predict the growth. The new computing law, Nevan’s Law, states that the processing power of the quantum computer will grow at a “doubly exponential rate” compared to classical computers. Though this law is not set in stone, it still gives way to thinking about the potential power of the quantum computer.
Every year, technology has grown and evolved to the point where your television is smart, your phone is smart, and even your watch is smart. “As we make these quantum computing chips smaller and smaller, trust me, every small thing you go to hold, tomorrow your pen will be smart, tomorrow your shoes will be smart, and tomorrow your phone will be smarter,” says Mr. Kalluru, “Tomorrow, your clothes might be smart. It might tell you your body temperature is not regulating correctly, or your odor is bad. Or, they might have body odor cancellation or something, I don’t know. There’s no limit to what we can think of.”
Wiweeki Predicts the Future of Quantum Computing
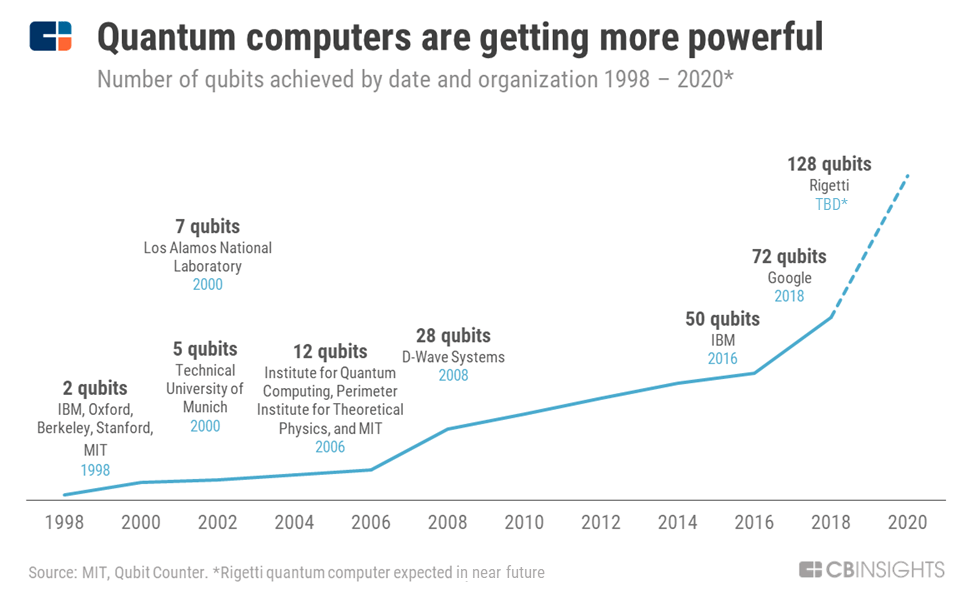
The problem that we are facing today is that the availability of hardware to create quantum computers is scarce. However, Wiweeki predicts that in the next 2-3 years, the IBMS and Googles are building the quantum computer and companies will be able to buy them for about $100,000. “Right now, you’d probably spend millions to buy one. It’ll come down to $100,000 level, and then maybe in 5 years it’ll come down to the $10,000 level,” says Mr. Kalluru, “Once it’s available, people will start jumping towards it.” He predicts that the data centers that are holding extremely large servers will be the first to buy and implement quantum computers, and in 10 years, every data center will be leveraging quantum computers.
As far as the general public, he says “If quantum computers could be in the reach of normal citizens, then within the next five years, that will penetrate into every device that you’re looking at. Everything will get scaled up.”
Mr. Kalluru is extremely fascinated with the technological evolution of growth. He states that:
“Ten years ago, high school kids were taught web development. By the time they graduated, they knew how to build websites. Then, five years ago, high school students were able to build mobile applications. In the current world, there are kids coming out of high school that are being taught machine learning and AI. So, in the next five years, high schoolers will be talking quantum computers, or will be programming using quantum computers.”
Even though quantum computers are in its early stages, Mr. Kalluru claims it is extremely possible that we will be leveraging fully functional quantum computers by the 2030s.
Conclusion
Quantum computers are an exciting, powerful, and mysterious emerging technology that everyone should know about because they have the potential to change the world.
“Quantum mechanics is just completely strange and counterintuitive. We can’t believe that things can be here and there at the same time. And yet, that’s a fundamental piece of quantum mechanics. So then the question is, life is dealing us weird lemons, can we make some weird lemonade from this?”
– Seth Lloyd, Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Physics at MIT
Here’s to the future!
Sources
Boixo, Sergio. “The Question of Quantum Supremacy.” Google AI Blog, Google, 4 May 2018, ai.googleblog.com/2018/05/the-question-of-quantum-supremacy.html.
Hajjar, Alamira Jouman. “Quantum Entanglement: What It Is & Why It Is Important in 2021.” AIMultiple, 11 Apr. 2021, research.aimultiple.com/quantum-computing-entanglement/.
ITIF, Technology Explainer. “Qubit vs Bit.” ITIF, 20 Sept. 2018, itif.org/publications/2018/09/20/itif-technology-explainer-what-quantum-computing.
Kaushal, Vivek. “Quantum Computer vs Supercomputer.” TecHindustan, Apr. 2018, techindustan.com/quantum-computing-explained-simply-how-quantum-computers-work/.
Komijani, Yashar. “Entanglement.” The Qubit Report, 8 Mar. 2020, qubitreport.com/quantum-computing-science-and-research/2020/03/08/do-humans-have-what-it-takes-to-apply-natures-quantum-entanglement-to-quantum-computing-rutgers-scientists-think-so/.
Leonhard, Gerd. “Evolution of Technology.” Gerd, 23 Oct. 2016, www.futuristgerd.com/2016/10/ready-abdicate-humanity-not-read-new-book-technology-vs-humanity/.
Marr, Bernard. “What Is Quantum Computing? A Super-Easy Explanation For Anyone.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 15 July 2017, www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2017/07/04/what-is-quantum-computing-a-super-easy-explanation-for-anyone/?sh=766559371d3b.
MIT. “Quantum Computers Are Getting More Powerful.” CBInsights, CB Information Services, 4 May 2020, www.cbinsights.com/research/report/tech-laws-success-failure/.
National Weather Service Forecast Office. “Station Model.” Wikipedia, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, 21 Dec. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Station_model.
Roser, Max, and Hannah Ritchie. “Transistor Count Over Time.” Wikipedia, Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, 8 July 2021, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore%27s_law.
Selwood, Dick. “Richard Feynman and Quantum Computing.” EEJournal, Techfocus Media, 24 May 2018, www.eejournal.com/article/richard-feynman-and-quantum-computing/.
Sharma, Siddharth. “The Ultimate Beginner\’s Guide to Quantum Computing and Its Applications.” Medium, Towards Data Science, 5 June 2020, towardsdatascience.com/the-ultimate-beginners-guide-to-quantum-computing-and-its-applications-5b43c8fbcd8f.
Sutter, Paul. “What Is Quantum Entanglement?” LiveScience, Future US , 26 May 2021, www.livescience.com/what-is-quantum-entanglement.html.
Vidar. “Google\’s Quantum Computer Is About 158 Million Times Faster Than the World\’s Fastest Supercomputer.” Medium, Predict, 28 Feb. 2021, medium.com/predict/googles-quantum-computer-is-about-158-million-times-faster-than-the-world-s-fastest-supercomputer-36df56747f7f.
Voorhoede, De. “Superposition and Entanglement.” Quantum Inspire, www.quantum-inspire.com/kbase/superposition-and-entanglement/.